As time progresses, the number of different types of electric bikes increases with the demand. Although reliable e-bikes are still somewhat of a new thing (let’s count in the past decade) there is still plenty of room for development, so let’s keep our eyes open.
Down below we’ve listed a bunch of different types of electric bicycles to get a brief overview of what’s out there. Check out our ebike guide down below to find answers to your questions.
Table of Contents
#1 E-Bike Motors
#2 E-Bike Drivetrains
#3 E-Bike Batteries
#4 The Different Types of E-Bikes 🏆
#5 E-Bike Classes
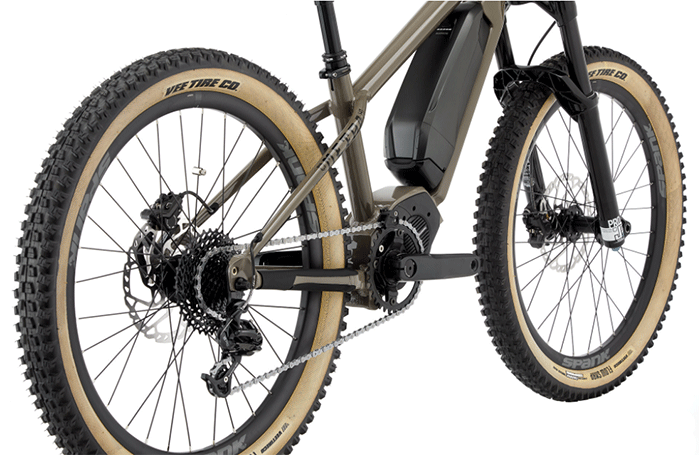
1. Electric Bike Motors

- Motor Types – Mid-drive, Hub motor, 2WD, Brushed / Brushless
- Motor Powers – 250W / 500W / 750W / 1,000W
Two main types of e-bikes come with either an e-bike motor placed in the bottom bracket (mid-drive) or in the rear wheel hub (hub motor).
On rare occasions, you’ll see e-bikes with a front-wheel drive, or two-wheel drive, also known as AWD e-bikes.
Hub drive e-Bike motors
Also known as the hub motor
- Wide-spread among affordable eBikes
*Except hunting eBikes, and some eRoad bikes that are equipped with a hub motor - Better direct torque levels due to more weight on the rear wheel
- Throttle option available (Which is great in case you’d snap a chain)
Mid-drive e-Bike motors
Also known as the direct-drive motor
- More economical
- Used on mid to high-end ebikes
- More natural ride feel due to better weight distribution
- Mainly pedal-assist
- Expensive
Related – Hub vs Mid-drive eBikes
2WD / All Wheel Drive e-Bike motors
- Motor on the front and rear hub for maximum traction
- Expensive all-terrain fat tire electric bikes
Important E-Bike Terminology
W = Watts. Motor power.
Average range:
- Mid-Drive: 250W
- Hub Motor: 750W
- 2WD: 1,000W+
Nm = Torque in Newton meters.
Average range: 40Nm – 100Nm
- 40Nm – City commuters, Single-speed eBikes.
Hub motor & mid-drive - 80Nm – Hub motor commuter bikes, mid-drive electric mountain bikes
Hub & Mid-drive - 100Nm – 160Nm – Rambo rear hub fat tire eBikes
Hub motor
Higher torque = More power and a noticeable ‘kick’ = Fast acceleration = Great for steep hills and on heavy fat tire ebikes.
- Related post: Best Ebikes for Hills
2. Electric Bike Drivetrains
- Almost all electric bicycles are equipped with a single front chainring.
- Most electric bikes are equipped with a derailleur & shifters
- Belt-drive e-bikes are great yet niché alternative to chain & sprocket drivetrain due to their quiet, clean, and maintenance-free characteristics
- Internally geared eBike motors are popular among belt-drive eBikes’ motors (Rambo Megaton, Priority Current)
3. Electric Bike Batteries

Electric bike batteries play one of the most important roles besides the bikes’ motor itself. What most electric bike brands are striving for – is the latest battery technology available. In most cases, what people are looking for the most in an e-bike is the range one can reach on a single ride.
Ah = Amp hour
Determines the capacity of the battery. More Ah = better battery life and range.
Average e-Bike battery range: 8-12ah
6.9V – 17Ah on a larger scale
V = Volt
Determines the force of the electric flow from the battery to the motor. More volts = more power to run from the battery to the. More voltage = more torque = not as economical.
Average e-Bike battery voltage: 36V – 48V
*30V to 52V on a larger scale
Wh = Watt-hour (Ah x V = Wh)
Battery capacity
Average range: 250Wh – 750Wh
*A popular e-bike brand Rad Pad Power Bikes have a 750W motor, and a 672Wh battery – estimated range between 20-45miles, depending on which mode has been used.
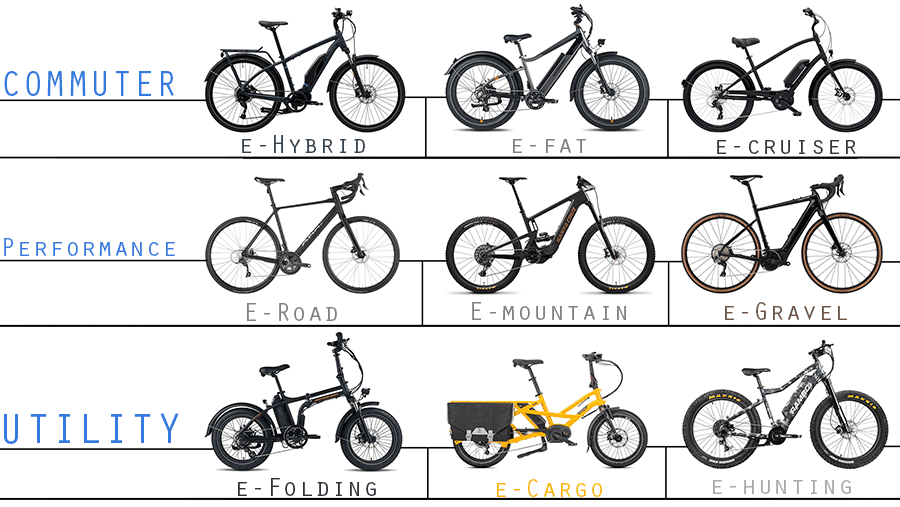
4. Different Types of Electric Bikes
Almost every single bike type has an electric version as well, but the three main eBike types are:
1. Commuter Bikes
2. Performance Bikes
3. Utility Bikes
1. E-bikes for commuting
EBikes to get you from A to B in comfort.
Hybrid – Comfortable & upright riding position, great for paved and light gravel roads.
Fat – 3″ to 5″ wide eBikes that have become popular due to their multifunctional field of use.
Cruiser – One of the most comfortable and laid-back bikes around.
City – Electric city bikes are the most basic to get around town.
2. Performance e-bikes
for training purposes
Electric Road Bikes – Generally Class 1 eBikes with max. assisted speed of 20mph. Great for going longer routes or hilly terrains.
Electric Mountain Bikes – Hardtail and full-suspensions with an extra oomph and suspension.
Electric Gravel Bikes – Fastest on/off road commuters.
3. Utility E-bikes
for hauling heavy loads, off-road riding, or multi-purpose bikes
Folding – Foldable eBikes must be one of the best-selling e-bike types on the market. What’s there not to like about a 20″ bike that fits a wide array of riders, and it can be folded compact
Cargo – Electric cargo bikes are bicycles that can be used for work, to haul pets and kids. E-Assisted motor on a e-cargo bike is usually stronger than on other types of ebikes.
Hunting – Mountain/Fat tire bike inspired eBikes that are also great for fishing
5. Electric Bike Classes
Class 1 eBike – Pedal-assisted electric bike.
Speed limited to 20mph.
Motor power limited to 750W.
Also known as a pedelec
Class 2 eBike – Throttle ebike with an optional pedal-assist
Speed limited to 20mph
Motor power limited to 750W
Class 3 eBike – Pedal-assist & optional throttle.
Speed limited to 28mph
Motor power limited to 750W
Class 4 eBike – Unlimited power & speed electric bikes with pedals.
Any eBike which has a higher assisted speed of 28mph, or power power over 750W is considered as a class 4 eBike.
Read More:
Electric Bike Rules & Regulations in the US
A Guide to Electric Bike Classes: Class 1, 2 & 3 Explained



